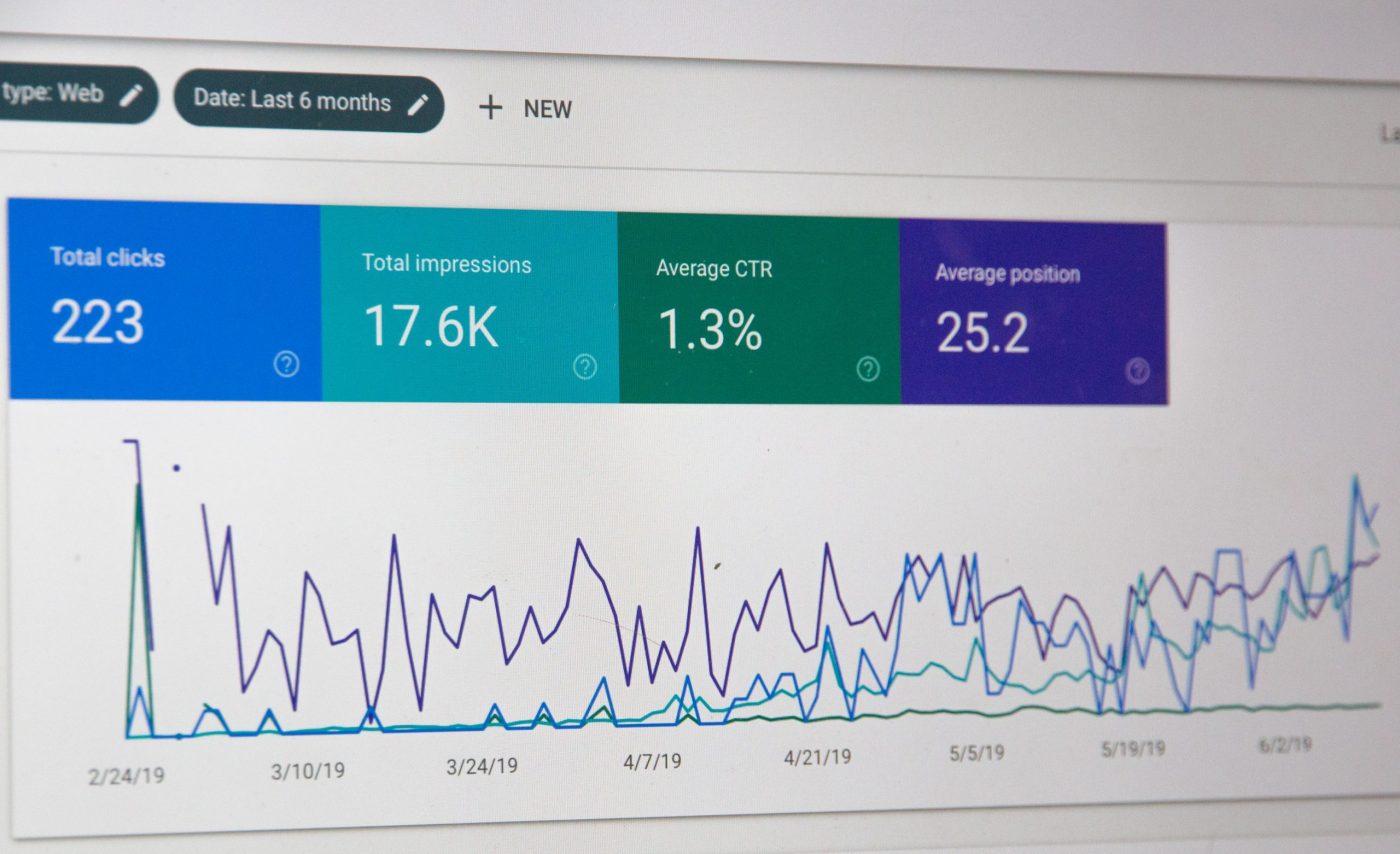
The world of SEO is always changing. It’s developing and adapting to make sure that it keeps up-to-date with what’s going on in the world – ensuring that the public can get all the information they need as quickly and efficiently as possible. That is the point of search engines, after all!
It is important to know how the on and offline world interact with each other, and how this will affect your website’s traffic and conversions.
When events impact search engines, you must be prepared. Some of these changes can happen organically, over a long time, and some are reactions to more specific events. To be able to market your business properly, having a good understanding of SEO is vital, knowing how people search at different times and how it can help you attract customers.
Here are some examples of recent events that have impacted SEO and the way that the internet is – and will be – used.
Google SOS Alerts
One of Google’s features is known as an SOS Alert. When something happens in the world where information needs to be given out, Google creates special search results which help spread this information. Recent situations that have warranted Google SOS Alerts include the tornados in Tennessee and Coronavirus.
A typical SOS Alert features a red box at the top of the screen, followed by ‘top stories,’ then a series of useful links followed by either local Twitter updates or the usual search results (pictured below), with authoritative sources taking the top rankings. They can also display information about how to donate to help to support relief efforts. All of this information is made clear, so that it’s easy to see and share with those also searching for the particular ‘SOS event.’
Coronavirus
Coronavirus is having a much more significant impact on the virtual world of SEO than you might have thought. This is due to how it’s affects on the outside world.
Some of the effects of Coronavirus on search and SEO include:
- More people searching and buying online as people self-isolate, spending less time outside
- Changes in what people are buying – face masks and hand sanitiser sales, for example, are going through the roof
- More people looking into how to stream events and communicate with colleagues online, from home
- An increase in people working from home
- Predictions of a slump in the travel industry, with fewer people searching for travel information and people looking into travel insurance
- The impact of a slower economy
All of this means that the trends of the search terms are different than usual, and you should try to take this into account when you are considering your content marketing strategy.
Elections and Political Advertising
In a world of fake news, micro-targeting and social media, political advertising can have a massive impact on society – especially in the outcome of elections and referendums. With the targeting of certain demographics of people, we have seen some political parties or viewpoints having a massive impact and the internet is really only just beginning to get to grips with this.
Media in its many forms has always played a big part in affecting how people see the world and ensuring that the media that we consume online is fair and true is vital.
In November 2019, for example, we saw Google announce that they were to ban political advertisers from targeting British voters except on characteristics of gender, age, and a rough geographical location in an attempt to create a balanced perspective for people.
Another way that elections have affected search trends is the nation’s quest for information. During the last election, for example, Google saw massive rises in searches for information about Jeremy Corbyn, party manifestos and what certain political parties stand for. It also saw surges in searches regarding how to leave the country after the election…
Changes in Copyright Law
The online use of content is an issue which the internet has never really got its head around. Whether it is a blatant forgery, the use of art and music without paying for it, or illegally downloading films, there is nowhere else in society where this is happening to such a level.
The EU has laid out a set of rules which are designed to help to prevent these – what many people consider to be – unethical practices, through their copyright reforms. The laws involve those who display snippets of material having to pay licensing fees, as well as forcing companies to police the content that they publish. It is important if you are carrying out any sort of content marketing, that you are fully up-to-date with these new laws.
Google had tested new SERPs to ‘try to understand what the impact of the proposed EU Copyright Directive would be to our users and publishing partners.’ The results looked sparse, like they hadn’t finished loading.
It’s predicted that the new laws will full roll out in 2021, meaning that next year will certainly be a memorable one for the internet.
As the world moves forward, we will always be coming up against new challenges. Whether it is a long or short term issue, it is important that for your business to succeed online, you keep updated on how these issues are impacting SEO.